Pressure Time Product (PTP)
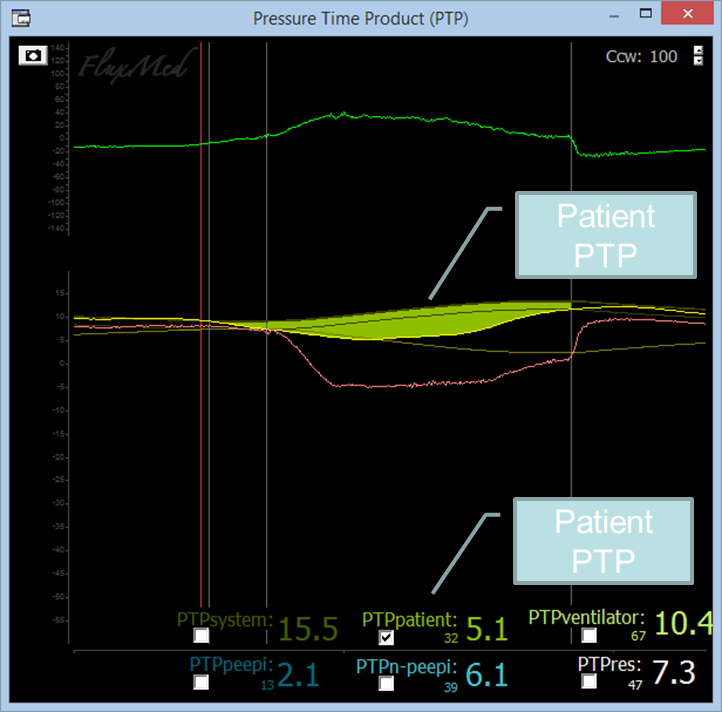
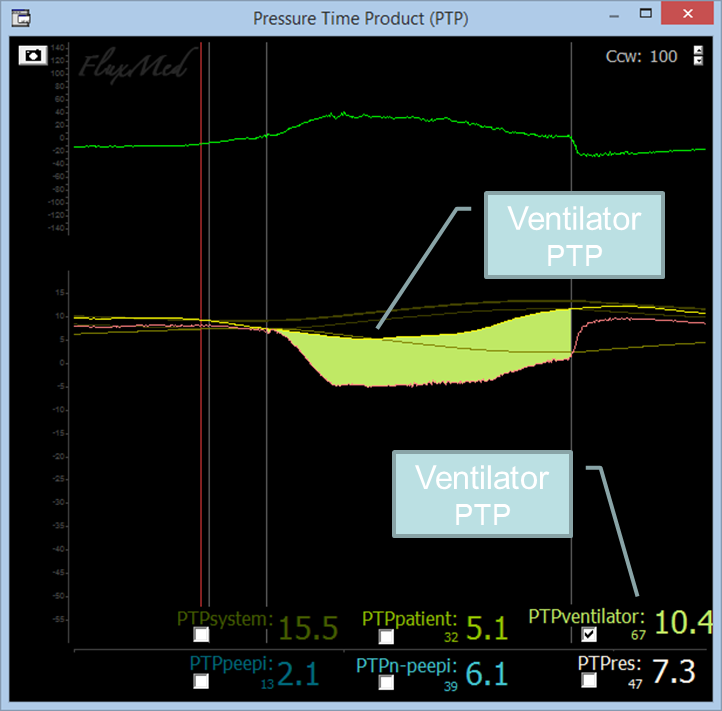
FluxMed respiratory monitors are the only monitors that calculate the pressure time product (PTP) breath by breath. The PTP quantifies the patient’s effort.
According to ATS and ERS recommendations on the evaluation of the respiratory muscles: the PTP, be it expressed for each breath or by minute, is the best tool for measuring the respiratory effort of ventilated patients (ATS/ERS Statement on Respiratory Muscle Testing, page. 613).
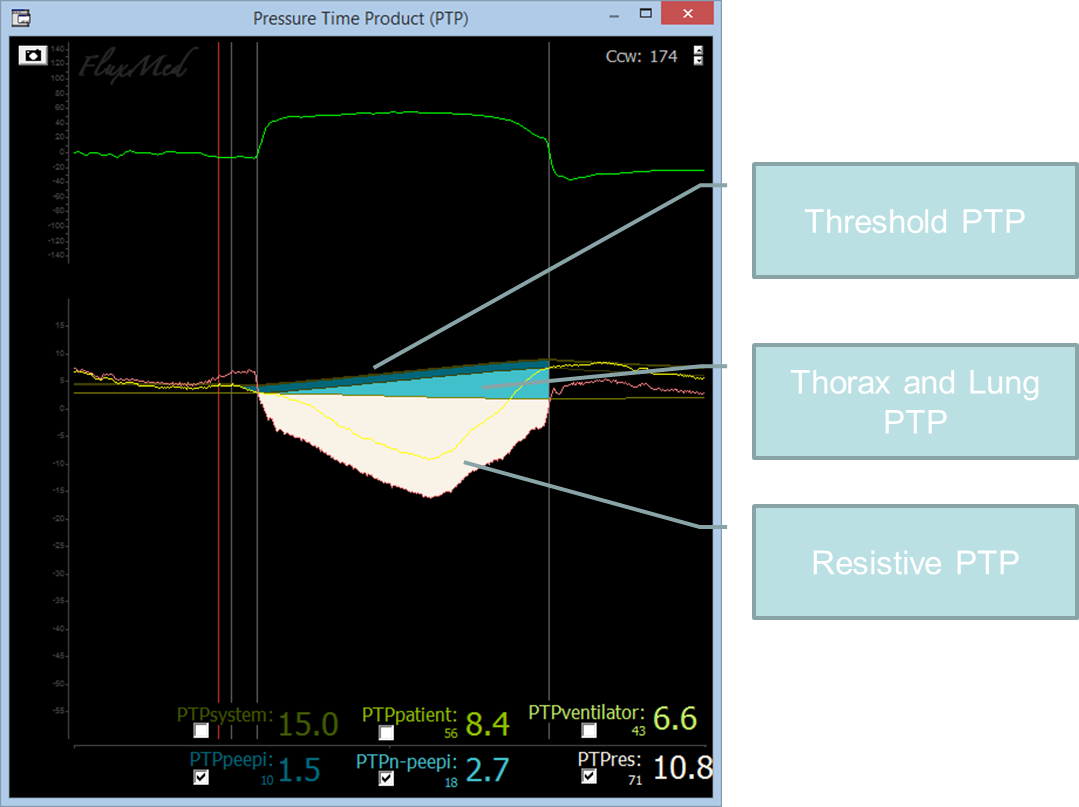
The PTP allows for the calculation of the patient’s effort on the three areas it comprises. One area corresponding to the patient’s resistive effort and two to the elastic one. The elastic effort is divided between the PEEPi-associated effort (intrinsic PEEP or AUTO PEEP) and the effort not associated to PEEPi, the thoracic-pulmonary elastic effort.
PTP and the equation of motion
The Pressure-Time Product (PTP) diagram allows you to quantify and visualize every component of the equation of motion: Paw + Pmus = PEEPi + E.V + R.F where:
- Paw is airway pressure variation over PEEP
- Pmus is the muscular pressure
- PEEPi is the intrinsic PEEP
- E and R are the patient's respiratory elastance and resistance
- V is for volume
- F is for flow
On the left side of the equation of motion we have the pressure sources (so, the pressure added by the patient and the ventilator).
The patient's Pmus is the area between the chest wall recoil and the esophageal pressure (Patient PTP)